A domain model is not a data model: it uses more specialized concepts for better modeling accuracy. A domain model uses a data model in its implementation and when a communication in and out of the system occurs. Knowing the differences between the two and when a data model or a domain model is at play is important for dealing with domain complexity.
Modeling
A model is a description of something - often reality - using concepts, intended to solve a problem through its usage.
E.g. I like this example often used by Eric Evans of an earth map using the mercator projection.
mercator-map.jpg
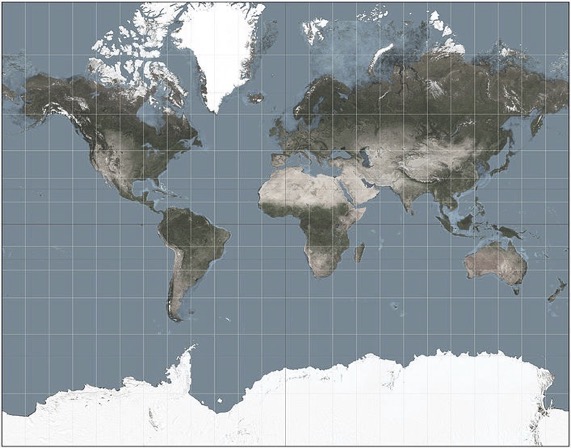
That’s a model! It describes the reality, the model is representative of it. Is this model accurate with reality? no…is this model useful? somehow but for who and for which usage? Let’s remember the particular projection, the one formalized by Mercator in 1569, From Wikipedia : “The Mercator projection was designed for use in marine navigation because of its unique property of representing any course of constant bearing as a straight segment.” ok, that model is wrong regarding of the countries area but useful when navigating.
All models are wrong, some are useful. George Box .
But let’s get back to our softwares composing Information Systems, we need to model the data and process used in it. More casualy a data model describes the information needs of a business. A map simplifies a complex geographic landscape in the same way that a data model simplifies a complex information landscape
An information system, composed of application manipulating data, is a model of a small, finite subset of the real world. So there is a correspondence between things inside the information system and things in the real world. Ideally, this would be a one-to-one correspondence, i.e., we could identify a single construct in the information system which represented a single thing in the real world.
Data model
There are several way to represent and structure data, from the simplest ones using only primitive data to the most sophisticated ones using entity-relation or object model. A data model categorizes concepts used by the domain users using concepts coming from its meta-model such as entitites, attributes and relations for the E/R Model .
There is several meta-models at our disposal for modeling data. The most used ones are E/R model, UML class diagram or more recently JSON with its schema capability .
Logical descriptions are more in terms of the information content of the database: the kinds of entities, the attributes, and the relationships among them. TODO : check out of the tar pit for logical and physical data model.
Entity/Relation Model
Conceptual and physical model
A conceptual data model has no programming language or database concerns in it. A physical data model represents the underlying technology, it uses the exact datatypes allowed by the technology and can have all the details regarding the data representation.
A conceptual model is detached of any implementation details, hence its form is durable.
We often encounter Exit logical model
Domain model
A domain model use more diverse concepts to specialize the concepts encountered in an information system: entities of course, but also value, service, rules, command, query, events, etc.
Domain model structure data but also the behavior thanks to concepts like command or event.